1. Restoration to Eco Park from Waste Dumping Site
The Nanjido was a small island where orchids and gromwell grew with various seasonal flowers. However, the Nanjido had been changed into a garbage dumping site for the city of Seoul, the capital of Korea, from 1978. Korea did not have any modern landfill techniques to treat the landfill gas and leachate during 1970s. The dumping site was used for 15 years without even covering the garbage with soil. Finally, after two 100m high garbage heaps, a total 92,000,000㎥ of garbage, were made, its use as a waste dumping site was finished in 1993. The Seoul city government (SCG) carried out landfill stabilization work and park establishment construction in consecutive order. Through the stabilization stage, the waste layer was blocked off from outside and facilities were installed in order to treat landfill gas and leachate generated from waste degradation. During the park construction stage, the Haneul Park and the Noeul Park were built on top of garbage mountain, while the Pyeonghwa Park and Nanjicheon Park was built on flatland and the Nanji Han River Park was built on riverside of the Han River. One year after closure of the dumping site in 1994, 89 species from 24 families of plants were discovered, but the numbers were rapidly increased as much as 502 species of 95 families of vegetation by 2010 since establishment of the World Cup Park.The City of Seoul already had the Olympic Park to memory 1988 Seoul Olympic Game. The Nanjido Eco Park is neighboring 2002 World Cup Stadium. So the park was named the World Cup Park. After the Nanjido was transformed into the World Cup Park there was also an increase of animal life including birds, insects, amphibians, fish and mammals. There were 167 species of animals discovered prior to construction of the World Cup Park and they included fish, amphibians, insects and mammals. However, eight years after the World Cup Park was completed, it grew to 731 species in 2010. The SCG has conducted natural ecosystem monitoring annually since 2002 and released annual reports by World Cup Park.View
[Animals and Plants Discovered at World Cup Park]
| Section |
Before 2000 |
2003 |
2005 |
2008 |
2010 |
| Plants |
60 families
271 species |
68 families
438 species |
90 families
485 species |
77 families
453 species |
95 families
502 species |
| Wild Birds |
21 families
33 species |
29 families
56 species |
29 families
57 species |
28 families
55 species |
33 families
70 species |
| Amphibians/Reptiles |
6 families
8 species |
9 families
13 species |
8 families
9 species |
9 families
14 species |
6 families
9 species |
| Land Insects |
53 families
114 species |
51 families
233 species |
62 families
267 species |
82 families
322 species |
101 families
516 species |
| Aquatic Invertebrates |
7 families
9 species |
- |
27 families
37 species |
36 families
48 species |
39 families
62 species |
| Fish |
- |
6 families
15 species |
6 families
10 species |
7 families
14 species |
6 families
10 species |
| Mammals |
2 families
3 species |
9 families
11 species |
8 families
9 species |
5 families
8 species |
8 families
10 species |
Source: World Cup Park, http://ebook.seoul.go.kr/Viewer/S4MQTB1YEELC.
2. Eco Park Construction linked with the 2002 World Cup
It was June 1996 when Korea and Japan were confirmed to co-host the 2002 FIFA World Cup and thus, the decision to build the Seoul World Cup Stadium near the Nanjido was made in October 1997 with just four years and eight months left to the start of the 2002 World Cup. From the aspect of 2002 World Cup clock, construction of the stadium was the most urgent and improvement of environmental factors near the stadium was also an important matter. One unchanging condition was that the Nanjido dumping site must be renovated before start of the World Cup game no matter what happens. The SCG mobilized all administrative powers and resources, maintained a simple decision-making structure, and finally completed designs and construction for landfill stabilization and ecological park on schedule before the start of the World Cup games.
[Major Project Periods of the Nanjido Area]
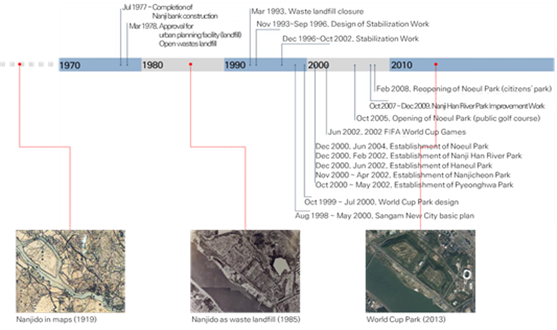
Source : Seoul City Government, https://seoulsolution.kr/ko/content/%EB%82%9C%EC%A7% 80%EB%8F%84-%EC%83%9D%ED%83%9C%EA%B3%B5%EC%9B%90-%EC%A1%B0%EC%84%B1%EC%82%AC%EC%97%85.
An Urban Open Space and Park
The SCG planned to create a new sub-center of Seoul metropolis at SangAm area in which residence, traffic system, hi-tech industries and ecology could harmonize in the future, calling it the New Millennium Town.World Cup Park is a part of SangAm area of Mapo local district in Seoul, where had been remained a backward reign of Seoul until the late 1990s. Further information about the New Millennium Town Plan is available from attached file.View With opening of the World Cup Park in 2002 and the reopening of the Noeul Park in 2008, plan to construct Seoul's SangAm New Millennium Town Park was completed for the most part.Contents and shape of World Cup Park was materialized in New Millennium Park Basic Plan.View In particular, it was possible to secure 43% of total area of the SangAm New Millennium Town as open spaces and parks. Twelve years after completion of the World Cup Park, residential areas as well as IT companies and high-tech industry have continuously moved into the town and it has now appearance of the SangAm New Town as planned originally. The establishment of the World Cup Park led to the creation of a new rest area and green space loved by residents of Seoul city. There are 12 million people who visit World Cup Park every year, thus out-numbering total number of people living in Seoul, which are 10.39 million people. It also has effect of expanding the rest area of the Seoul city by 5.3%.
[Visitors to World Cup Park]

Source: Google Images(Search word=World Cup Park)